Real-Time SDK - C/C++
RTSDK (EMA/ETA) Quick Start
| Last update | Aug 2024 |
| Environment | Windows, Linux |
| Compilers | Visual Studio (Windows), GCC (Linux) Refer to RTSDK Readme for a complete list. |
| Prerequisites (Desktop access) | The steps outlined within this guide depend on details outlined within the RTSDK C/C++ Installation Guide available within GitHub. Ensure this document is at your disposal. Access to an existing LSEG Real-Time Distribution System to retrieve content |
| Prerequisites (Amazon EC2 access) | Set Up an Amazon EC2 instance based on the AMI. |
Important Note: If you are using the Wealth solution (Pricing Streaming Optimized Service or Pricing Streaming Service), the products currently support Authentication Version 1 only (As of May 2024). Please contact your LSEG representative to verify if you are using Wealth or RTO solution.
Introduction
The goal of this Getting Started tutorial is to provide the developer with the steps required to confirm access to either a deployed LSEG Real-Time Distributed System (RTDS) or the cloud-based LSEG Real-Time - Optimized (RTO) service by executing one of the packaged RTSDK examples. EMA and ETA are sub-components of the RTSDK (Real-Time SDK) package that includes a number of examples available to test specific functionality. For our purposes, the goal is to walk through the procedure to specify the connection details to access the preferred streaming platform, retrieving market data content.
This guide is applicable to both Linux and Windows environments.
Additional Details on the prerequisites
To access LSEG Real-Time -- Optimized, you should have a v1 authentication (Machine ID) or v2 authentication (Service account). These authentication accounts are used to get tokens. Then the tokens can be used to login to LSEG Real-Time – Optimized. For more information regarding v1 and v2 authentication, please refer to the Account authorization V1 to V2 migration cheat sheet article.
The v1 authentication comprises of:
- Machine ID: A username in the form of GE-A-XXXXXXXX-X-XXXX
- Password: A password for the machine ID
- Client ID: A client ID or App Key that can be generated by using the AppKey Generator
The v2 authentication comprises of:
- Client ID: A public identifier for apps
- Client Secret: A secret known only to the application and the authorization server
Note: The client_id in the v2 authentication is not the same value as the client_id in the v1 authentication which is an app key.
Please find more detail from the following resources about the v2 authentication.
- Changes to Customer Access and Identity Management: LSEG Real-Time - Optimized
- Getting Started with Version 2 Authentication for Real-Time: Overview
Alternatively, if you want to test access to a deployed RTDS environment, your market data administrator can grant you permission and provide you with a user ID.
If accessing services via LSEG Real-Time - Optimized, this requires an encrypted connection. The C/C++ libraries utilize OpenSSL for encryption. Refer to the C/C++ readme for details related to OpenSSL.
Note: After June 2024, the V1 authentication is only available for Wealth users. RTO uses must migrate to the v2 authentication.
Download the RTSDK (Desktop access only)
The Enterprise Message API (EMA) and Enterprise Transport API (ETA) are included in the RTSDK package. Within the RTSDK C/C++ Installation Guide, you can refer to the sections to obtain the download package.
Once the package has been downloaded and installed, we need to generate the project files necessary to build our desired examples. The C/C++ package depends on the CMake utility and the bundled configuration files to configure a built Tree. Refer to the CMake section outlined within the installation guide to configure a build tree for either a Windows or Linux environment.
# Example cmake command on Windows using Visual Studio 2022
C:\tmp\RTSDK-2.2.0.L1.win.rrg> cmake -H. -Bbuild -G "Visual Studio 17 2022" -A x64
On Windows PowerShell, the following command can be used.
PS C:\tmp\RTSDK-2.2.0.L1.win.rrg> cmake -S. -Bbuild -G "Visual Studio 17 2022" -A x64
Otherwise, the absolute source path can be used with the -H parameter. Howeover, the source path must not contain white spaces.
PS C:\tmp\RTSDK-2.2.0.L1.win.rrg> cmake -H"C:\tmp\RTSDK-2.2.0.L1.win.rrg" -Bbuild -G "Visual Studio 17 2022" -A x64
Once completed, we can move to the Build and Run an example section below.
Build and run an example
To demonstrate the basic operation of streaming data, you can choose to build and run any of the following relevant examples available within the RTSDK package:
- For EMA, the following are available:
- Cons113 [113_MP_SessionMgmt] - example to test connectivity into RTO
- Cons100 [100_MP_SessionMgmt] - example to test connectivity into a deployed RTDS
- For ETA, the following is available:
- VAConsumer - example tests connectivity into both RTO and RTDS
Depending on your target OS (Windows or Linux), refer to the installation guide for details of the location of the generated project files. Once you've determined the main project file as outlined within the guide, choose the desired example (EMA or ETA) and build.
For example:
Windows: Within the main project file (rtsdk), simply locate and build your desired example.
Linux:
# From your build directory, eg: rtbuild
# EMA - RTO (cloud)
make Cons113
# EMA - RTDS (deployed)
make Cons100
# ETA - Both RTO and RTDS
make VAConsumer
*Important*: Prior to running some of the examples, we must ensure the required external libraries are properly referenced. For a list of external dependencies, refer to the C/C++ readme.
Within the RTSDK download package, the installdb directory includes external libraries (including libcurl). Some of the examples may require the need to reference the external dependencies within your setup. For example, use LD_LIBRARY_PATH for Linux or make sure that the libraries are otherwise accessible for Windows (e.g., include the directory in %PATH%).
# Example (Windows)
setx PATH "%PATH%;sourcdir\installdb\WIN_64_VS143\lib
# Example (Linux)
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=builddir/install/lib64
Once configured, you are ready to run an example.
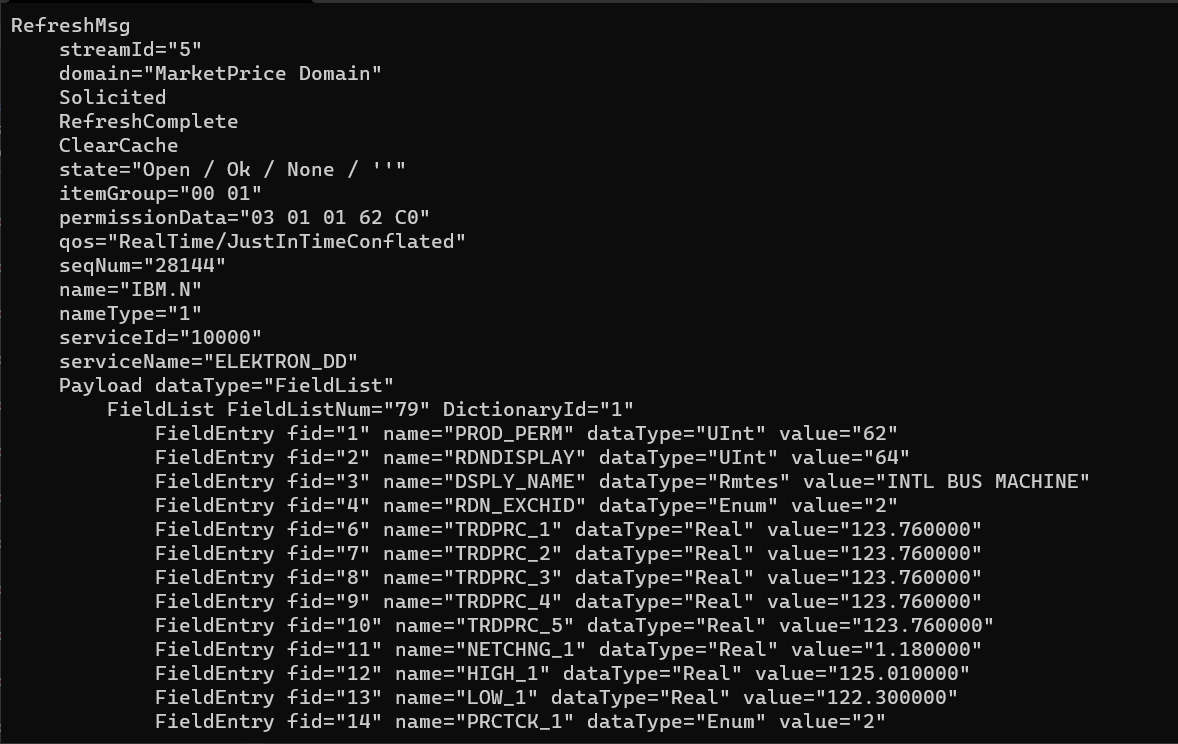
When running any of the following examples, the goal is to generate output showing market data. For example:
EMA
The EMA examples will require additional steps prior to running:
Cons100 (deployed test against RTDS):
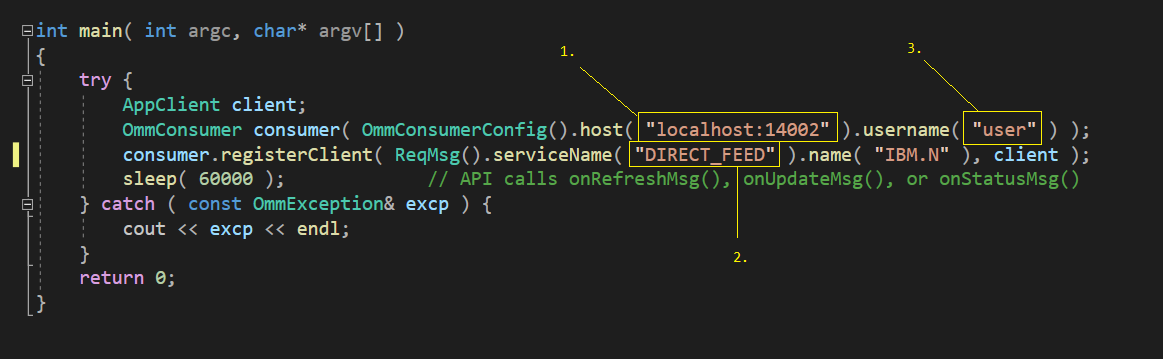
Within your sourceDir/Cpp-C/Ema/Examples/Training/Consumer/100_Series/100_MP_Streaming directory, edit the Consumer.cpp file:
Modify the required values:
- Choose the location of your deployed RTDS. Eg:'ads:14002'
- Change the name of the service providing market data. Eg: 'ELEKTRON_DD'. Note: Reach out to the market data team for this setting.
- If applicable, choose your ID provided by your market data team.
# Navigate to the binary directory and execute the example
# Windows Eg: sourceDir/Cpp-C/Ema/Executables/WIN_64_VS143/Debug_MDd
Cons100
# Linux: Eg: sourceDir/Cpp-C/Ema/Executables/RHEL8_64_GCC831/Optimized
./Cons100
Cons113 (RTO test):
This example requires the EMA configuration file: EmaConfig.xml to be copied within the runtime directory.
# Navigate to the binary directory and copy the config file
# Windows Eg: sourceDir/Cpp-C/Ema/Executables/WIN_64_VS143/Debug_MDd
copy ..\..\..\EmaConfig.xml .
# Linux: Eg: sourceDir/Cpp-C/Ema/Executables/RHEL8_64_GCC831/Optimized
cp ../../../EmaConfig.xml .
Connecting to RTO with the V1 authentication
# Run the example - connecting into RTO
# Note: Ensure you have the credentials as outlined within the Pre-requisite section above
# Windows example
Cons113 -username GE-X-01234567-8-9999 -password my_password -clientId f6698eeeeexxxxx8888811111eeee12345
# Linux example
./Cons113 -username GE-X-01234567-8-9999 -password my_password -clientId f6698eeeeexxxxx8888811111eeee12345
Connecting to RTO with the V2 authentication
# Run the example - connecting to RTO with V2 authentication
# Note: Ensure you have the credentials as outlined within the Pre-requisite section above
# Windows example
Cons113 -clientId GE-XXXXXXXXXXXX -clientSecret <client_secret>
# Linux example
./Cons113 --clientId GE-XXXXXXXXXXXX -clientSecret <client_secret>
ETA
The following ETA example does not require additional configuration. In addition, the same example can be used to connect to both a deployed RTDS and a cloud-based RTO environment.
# Ensure you are running from the runtime directory
# Windows: Eg: sourceDir/Cpp-C/Eta/Executables/WIN_64_VS143/Debug_MDd
# Linux: Eg: sourceDir/Cpp-C/Eta/Executables/RHEL8_64_GCC831/Optimized
# Run the example - connecting into a deployed RTDS
VAConsumer -tcp ads:14002 ELEKTRON_DD mp:AAPL.O
# Run the example - connecting to RTO with the V1 authentication
# Note: Ensure you have the credentials as outlined within the Pre-requisite section above
VAConsumer -encryptedSocket us-east-2-aws-3-med.optimized-pricing-api.refinitiv.net:14002 ELEKTRON_DD mp:IBM.N -uname GE-X-01234567-8-9999 -passwd my_password -clientId f6698eeeeexxxxx8888811111eeee12345 -sessionMgnt
# Run the example - connecting to RTO with the V2 authentication
VAConsumer -encryptedSocket us-east-2-aws-3-med.optimized-pricing-api.refinitiv.net:14002 ELEKTRON_DD mp:IBM.N -clientId GE-XXXXXXXXXXXX -clientSecret <client_secret> -sessionMgnt
Troubleshooting
Error: Exception Type='OmmInvalidConfigurationException', Text='OmmConsumerConfigImpl::consumerName parameter [Consumer_4] is a non-existent consumer name'
Reason: No EMA config file. The EMA example 'Con113' depends on the config file: EmaConfig.xml to be available within the working directory.
---------------------------------
Error: Error Text Failed to initialize RsslRestClient. Text: <..../Real-Time-SDK/Cpp-C/Eta/Impl/Util/rsslCurlJIT.c:77> Error: 0012 Libcurl intialization failed. Curl library: libcurl.so not found.
Reason: Not referencing external libraries. The example you are using must reference the external libraries by either updating your PATH (Windows) or LD_LIBRARY_PATH (Linux). Refer to the "Build and Run an example" section defined above.
--------------------------------
Error: 0012 Unable to load openSSL Libraries
Reason: OpenSSL not installed. Refer to the Pre-requisite section defined above.
--------------------------------
Error: Error Text <..../Real-Time-SDK/Cpp-C/Eta/Impl/Transport/rsslSocketTransportImpl.c:6074> Error: 1002 ipcConnecting() client connect() failed. System errno: (107) loggerMsgEnd
Reason: The RTDS server you are connecting to may be invalid or incorrectly specified. Reach out to your market data team to confirm the server IP address.
--------------------------------
Error: Connection down, reconnecting. Channel fd=18446744073709551615
Error text: <D:\Jenkins\workspace\ESDKCore_RCDEV\OS\VS142-64\rcdev\source\rtsdk\Cpp-C\Eta\Impl\Transport\ripcsslutils.c:1748> Error: 1002 ripcSSLInit client connect() failed. System errno: 10057
Reason: Cannot reach the endpoint or server specified. For example, when connecting to:
- RTO (cloud)
The specified -encryptedSocket is either invalid or you may not have access to the specified tier. To retrieve a valid list of RTO endpoints based on your assigned tier, refer to the DNS Names within the Current Endpoints section outlined in the LSEG Real-Time - Optimized Installation and configuration for client use documentation.
- RTDS (deployed)
The specified deployed server -tcp is unavailable or incorrect. You will need to confirm with your market data team the correct address and ensure you have access.
Next Steps
Once you have successfully completed the steps above, you can further your learning by following the series of tutorials.