Author:

Application resilience refers to an application's ability to handle unexpected issues within its components while continuing to deliver its services. In the financial sector, resilience is a cornerstone of reliability and trust. Therefore, when designing and developing applications, developers must prioritize resilience to ensure uninterrupted performance. For real-time financial applications, resilience means the ability to swiftly receive real-time data for all subscribed instruments with minimal data loss, even during unforeseen disruptions such as server disconnections or service outages.
Fortunately, the Real-time SDKs are built with resilience in mind, offering support for connection recovery through a range of methods, from basic to advanced. For example, the SDKs support features such as connection recovery, failover, warm standby, and the latest addition—preferred host.
This article introduces the Preferred Host feature, which was added in RTSDK C++/C Release 2.2.3.L1 (EMA/ETA 3.8.3.L1), RTSDK Java 2.3.1.L1 (EMA/ETA 3.9.1.L1 aka 3.9.1.0) and later, as of the time of this writing. This feature enables consumer applications to designate a preferred host and trigger a non-disruptive connection attempt.
Preferred Host feature
The Preferred Host feature allows consumer applications to designate a specific host or warm standby group as the preferred connection. When configured, the APIs can switch back to the preferred host or preferred warm standby group based on a timer or a direct function call. This feature is available in EMA via configuration settings, and in ETA Value Added—regardless of whether the watch list is enabled. This feature is unsupported for both Non-Interactive and Interactive Providers. It can typically be applied in the following four scenarios.
1. Failover
The Real-Time SDKs allow users to specify multiple channels through configuration or code. If the current channel becomes disconnected, the SDKs will automatically fail over to the next available channel using a round-robin method. The newly connected channel remains active until it is also disconnected.
This failover approach is generally suitable for most scenarios. However, in situations where a primary-backup channel structure is preferred, users may want the application to consistently attempt to reconnect to the primary channel after switching to a backup. With this preferred behavior, the SDKs will periodically check the status of the primary channel and automatically switch back to it once it becomes active, as shown in the picture below.
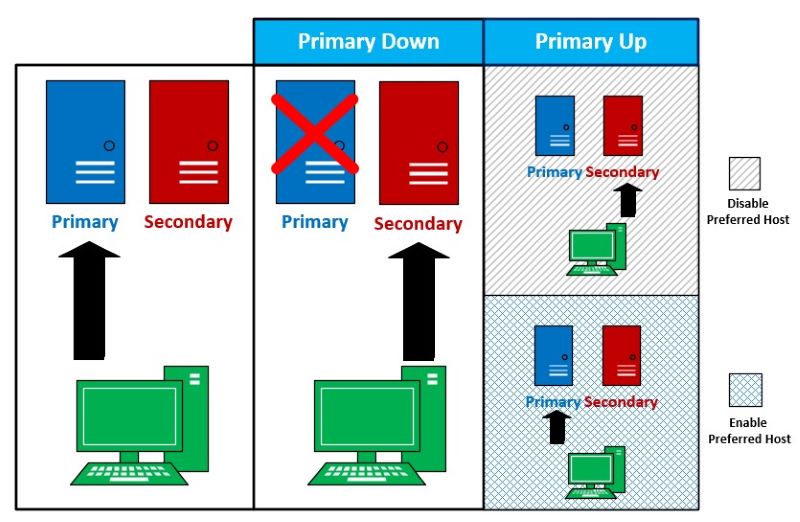
2. Warm Standy
The Real-Time SDKs also support the Warm Standby feature. With this feature, the SDKs establish multiple connections to servers—one to an active server and others to standby servers. When the active connection fails or a service on the active server becomes unavailable, the SDKs promote one of the standby connections to active and continue retrieving data from it. If the starting active server or its service becomes available again, the SDKs re-establish a connection to it, which then functions as a standby connection.
The Preferred Host feature can also be used in conjunction with Warm Standby. When the starting active server or its service becomes available, the SDKs will prioritize it and use it as the active server, as shown in the picture below.
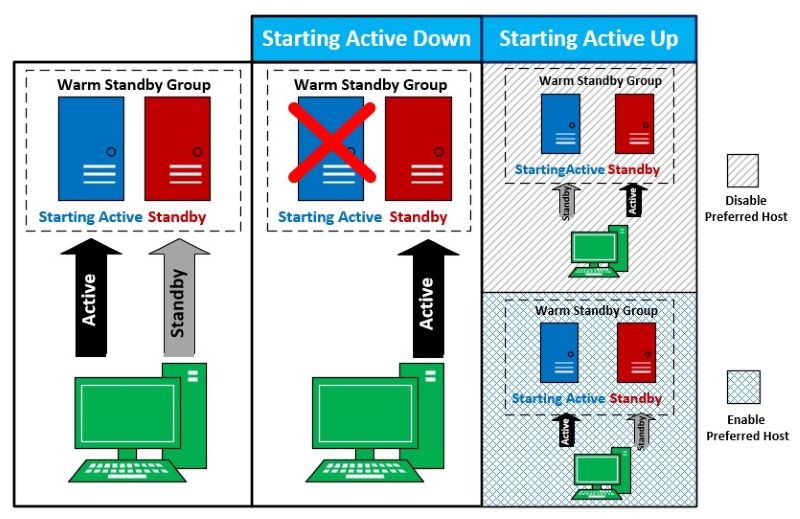
3. Warm Standby Groups
The Real-Time SDKs allow developers to configure multiple warm standby groups through code or configuration files. If all servers in the currently active group become unreachable, the SDKs automatically fail over to the next available group using a round-robin strategy. The newly connected group remains active until all its services are also unavailable, at which point the SDKs continue the failover process.
With the preferred host feature, developers can specify a preferred warm standby group. The SDKs will periodically check the availability of the starting active server in this group and automatically switch back to it once it becomes reachable, as illustrated below.
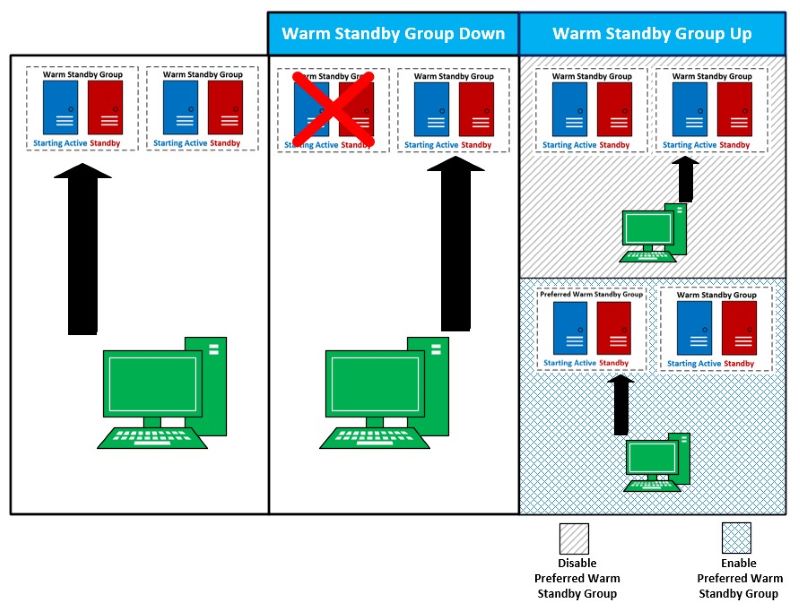
4. Request Routing
The Request Routing feature, implemented on the client side, allows applications to route market data item requests across multiple connections based on the availability of services on each one. Each connection can be configured to support failover, warm standby, warm standby groups, and the preferred host feature, providing flexible and resilient request handling.
Note: The request routing is only available in EMA.
Preferred Host Operation Trigger
When the Preferred Host feature is enabled, the SDKs provide two fallback mechanisms to connect to the preferred host or a warm standby group: a function call and a time-based interval.
1. Function Call
The SDKs offer functionality to trigger the preferred host fallback mechanism. In EMA, this is done using the OmmConsumer::fallbackPreferredHost() method, while ETA Value Added provides the rsslReactorFallbackToPreferredHost() method for the same purpose. For implementation details, refer to the 502_PH_ChannelInfo and VAConsumer examples, respectively, to see how these methods are invoked.
2. Time Interval
The SDKs also allow applications to trigger the preferred host fallback mechanism by configuring a timer using either a time-of-day cron string format or a specific time interval (in seconds). In EMA, this is achieved through the PHDetectionTimeSchedule and PHDetectionTimeInterval configuration options, respectively. In ETA Value Added, the mechanism is configured via the RsslPreferredHostOptions.detectionTimeSchedule and RsslPreferredHostOptions.detectionTimeInterval fields. When both configurations are specified, the cron-based time-of-day setting takes precedence over the interval-based configuration.
A cron expression is a string composed of five or six fields, each specifying a particular aspect of the schedule.
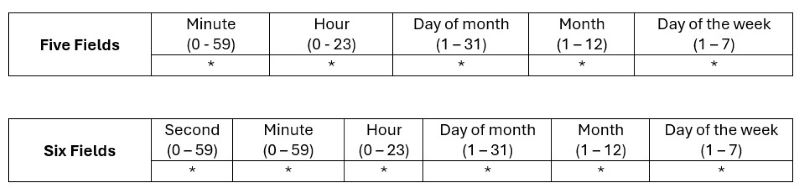
The sample cron expressions are:
| #Fields | Cron Expression | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 * * * * | Trigger at the 10th minute of every hour |
| 5 | 15 10 * * * | Trigger at 10:15 AM every day |
| 5 | */5 * * * * | Trigger every five minutes |
| 5 | 0 */2 * * * | Trigger every two hours |
| 6 | 30 * * * * * | Trigger at the 30th second of every minute |
| 6 | 30 10 * * * * | Trigger at 10th minute and 30th second of every hour |
| 6 | */30 * * * * * | Trigger every 30 seconds |
EMA Sample Configurations
EMA supports the Preferred Host feature through configurable settings, allowing users to modify application behavior by updating these configurations.
1. Preferred Host with Failover
The following configurations define Consumer_9, which sets the ChannelSet to use Channel_1 and Channel_7 for failover. Channel_1 is designated as the preferred host and it uses a time-based interval of 30 seconds to trigger the preferred host fallback mechanism.
<ConsumerGroup>
<DefaultConsumer value = "Consumer_9"/>
<ConsumerList>
<Consumer>
<Name value="Consumer_9"/>
<ChannelSet value="Channel_1, Channel_7"/>
<Logger value="Logger_2"/>
<Dictionary value="Dictionary_2"/>
<EnablePreferredHostOptions value="1"/>
<PreferredChannelName value="Channel_1"/>
<PHDetectionTimeInterval value="30"/>
</Consumer>
</ConsumerList>
</ConsumerGroup>
2. Preferred Host with Warm Standby
The following configurations define Consumer_9, which sets the WarmStandbyChannelSet to WarmStandbyChannel_1. The initial active server, Channel_1, is designated as the preferred host and it uses a cron expression to trigger the preferred host fallback mechanism every 30 minutes.
<ConsumerGroup>
<DefaultConsumer value = "Consumer_9"/>
<ConsumerList>
<Consumer>
<Name value="Consumer_9"/>
<WarmStandbyChannelSet value="WarmStandbyChannel_1"/>
<Logger value="Logger_2"/>
<Dictionary value="Dictionary_2"/>
<EnablePreferredHostOptions value="1"/>
<PHFallBackWithInWSBGroup value="1"/>
<PHDetectionTimeSchedule value="*/30 * * * *"/>
</Consumer>
</ConsumerList>
</ConsumerGroup>
…
<WarmStandbyGroup>
<WarmStandbyList>
<WarmStandbyChannel>
<Name value="WarmStandbyChannel_1"/>
<StartingActiveServer value="Server_Info_1"/>
<StandbyServerSet value="Server_Info_2"/>
<WarmStandbyMode value="WarmStandbyMode::LOGIN_BASED"/>
</WarmStandbyChannel>
</WarmStandbyList>
</WarmStandbyGroup>
…
<WarmStandbyServerInfoGroup>
<WarmStandbyServerInfoList>
<WarmStandbyServerInfo>
<Name value="Server_Info_1"/>
<Channel value="Channel_1"/>
<PerServiceNameSet value=""/>
</WarmStandbyServerInfo>
<WarmStandbyServerInfo>
<Name value="Server_Info_2"/>
<Channel value="Channel_7"/>
<PerServiceNameSet value=""/>
</WarmStandbyServerInfo>
</WarmStandbyServerInfoList>
</WarmStandbyServerInfoGroup>
3. Preferred Host with Warm Standby Group
The following configurations define Consumer_9, which set the WarmStandbyChannelSet to WarmStandbyChannel_1 and WarmStandbyChannel_2 for failover. WarmStandbyChannel_1 is designated as the preferred warm standby group and it uses a cron expression to trigger the fallback mechanism every 1 hour.
Note: The ReconnectAttemptLimit configuration is required for the preferred warm standby group and the PHFallBackWithInWSBGroup configuration must be disabled.
<ConsumerGroup>
<DefaultConsumer value = "Consumer_9"/>
<ConsumerList>
<Consumer>
<Name value="Consumer_9"/>
<WarmStandbyChannelSet value="WarmStandbyChannel_1, WarmStandbyChannel_2"/>
<ReconnectAttemptLimit value="5"/>
<Logger value="Logger_2"/>
<Dictionary value="Dictionary_2"/>
<PreferredWSBChannelName value="WarmStandbyChannel_1"/>
<EnablePreferredHostOptions value="1"/>
<PHFallBackWithInWSBGroup value="0"/>
<PHDetectionTimeSchedule value="0 */1 * * *"/>
</Consumer>
</ConsumerList>
</ConsumerGroup>
…
<WarmStandbyServerInfoGroup>
<WarmStandbyServerInfoList>
<WarmStandbyServerInfo>
<Name value="Server_Info_1"/>
<Channel value="Channel_1"/>
<PerServiceNameSet value=""/>
</WarmStandbyServerInfo>
<WarmStandbyServerInfo>
<Name value="Server_Info_2"/>
<Channel value="Channel_7"/>
<PerServiceNameSet value=""/>
</WarmStandbyServerInfo>
<WarmStandbyServerInfo>
<Name value="Server_Info_3"/>
<Channel value="Channel_11"/>
<PerServiceNameSet value=""/>
</WarmStandbyServerInfo>
<WarmStandbyServerInfo>
<Name value="Server_Info_4"/>
<Channel value="Channel_12"/>
<PerServiceNameSet value=""/>
</WarmStandbyServerInfo>
</WarmStandbyServerInfoList>
</WarmStandbyServerInfoGroup>
<WarmStandbyGroup>
<WarmStandbyList>
<WarmStandbyChannel>
<Name value="WarmStandbyChannel_1"/>
<StartingActiveServer value="Server_Info_1"/>
<StandbyServerSet value="Server_Info_2"/>
<WarmStandbyMode value="WarmStandbyMode::LOGIN_BASED"/>
</WarmStandbyChannel>
<WarmStandbyChannel>
<Name value="WarmStandbyChannel_2"/>
<StartingActiveServer value="Server_Info_3"/>
<StandbyServerSet value="Server_Info_4"/>
<WarmStandbyMode value="WarmStandbyMode::LOGIN_BASED"/>
</WarmStandbyChannel>
</WarmStandbyList>
</WarmStandbyGroup>
4. Preferred Host with Request Routing
The following configurations define Consumer_10, which utilizes the request routing feature. It establishes two connections through the SessionChannelSet configuration, with each connection comprising two channels for failover. The first channel of each connection is designated as the preferred host and employs a 30-second time-based interval to activate the preferred host fallback mechanism.
<ConsumerGroup>
<DefaultConsumer value = "Consumer_10"/>
<ConsumerList>
<Consumer>
<Name value="Consumer_10"/>
<SessionChannelSet value="Connection_1, Connection_2"/>
<SessionEnhancedItemRecovery value="1"/>
<Dictionary value="Dictionary_3"/>
</Consumer>
</ConsumerList>
</ConsumerGroup>
…
<SessionChannelGroup>
<SessionChannelList>
<SessionChannelInfo>
<Name value="Connection_1"/>
<ChannelSet value="Channel_1, Channel_7"/>
<EnablePreferredHostOptions value="1"/>
<PreferredChannelName value="Channel_1"/>
<PHDetectionTimeInterval value="30"/>
</SessionChannelInfo>
<SessionChannelInfo>
<Name value="Connection_2"/>
<ChannelSet value="Channel_11, Channel_12"/>
<EnablePreferredHostOptions value="1"/>
<PreferredChannelName value="Channel_11"/>
<PHDetectionTimeInterval value="30"/>
</SessionChannelInfo>
</SessionChannelList>
</SessionChannelGroup>
...
ETA Examples
ETA examples that support the preferred host feature are VAConsumer and MultiCredWL_Consumer.
1. Preferred Host with Failover
To use the preferred host feature with failover, run the VAConsumer example with the following command-line arguments. These arguments specify two servers—127.0.0.1:14002 and 127.0.0.1:14003—for failover. The first server (127.0.0.1:14002) is designated as the preferred host and uses a 30-second time-based interval to trigger the fallback mechanism.
-tcp 127.0.0.1:14002,127.0.0.1:14003 ELEKTRON_DD mp:IBM.N -enablePH -preferredHostIndex 0 -detectionTimeInterval 30
The following arguments are similar to the previous one but they use a cron expression instead.
-tcp 127.0.0.1:14002,127.0.0.1:14003 ELEKTRON_DD mp:IBM.N -enablePH -preferredHostIndex 0 -detectionTimeSchedule "*/30 * * * * *"
2. Preferred Host with Warm Standby
To use the preferred host with warm standby, run the MultiCredWLConsumer with the following content in the WSBConfig.json file.
{
"LoginMsgs": [
{
"Name": "Login1",
"UserName": "User1"
},
{
"Name": "Login2",
"UserName": "User1"
}
],
"WSBGroups": [
{
"WSBMode": "login",
"WSBActive": {
"Host": "localhost",
"Port": "14002",
"LoginMsgName": "Login1"
},
"WSBStandby": [
{
"Host": "localhost",
"Port": "14003",
"LoginMsgName": "Login2"
}
]
}
],
"PreferredHost": {
"enablePH": true,
"detectionTimeInterval": 30,
"fallbackWithinWSBGroup": true
}
}
The above configurations set an active server to localhost:14002 and a standby server to localhost:14003. The enablePH and the fallbackWithinWSBGroup configurations are enabled. It uses a 30-second time-based interval to trigger the fallback mechanism.
Then, run the example with the following command line arguments
-s ELEKTRON_DD -mp LSEG.L
3. Preferred Host with Warm Standby Group
To use the preferred host with warm standby group, run the MultiCredWLConsumer with the following content in the WSBConfig.json file.
{
"LoginMsgs": [
{
"Name": "Login1",
"UserName": "User1"
},
{
"Name": "Login2",
"UserName": "User1"
},
{
"Name": "Login3",
"UserName": "User1"
},
{
"Name": "Login4",
"UserName": "User1"
}
],
"WSBGroups": [
{
"WSBMode": "login",
"WSBActive": {
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
"Port": "14002",
"LoginMsgName": "Login1"
},
"WSBStandby": [
{
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
"Port": "14003",
"LoginMsgName": "Login2"
}
]
},
{
"WSBMode": "login",
"WSBActive": {
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
"Port": "14004",
"LoginMsgName": "Login3"
},
"WSBStandby": [
{
"Host": "127.0.0.1",
"Port": "14005",
"LoginMsgName": "Login4"
}
]
}
],
"PreferredHost": {
"enablePH": true,
"warmstandbyGroupListIndex": 0,
"detectionTimeSchedule": "*/30 * * * * *"
}
}
The above configurations set two warm standby groups and designate the first group as the preferred warm standby group. The enablePH is enabled. and it uses a cron expression to trigger the fallback mechanism every 30 second. Then, run the example with the following command line arguments.
-s ELEKTRON_DD -mp LSEG.L -reconnectAttemptLimit 5
Note: The reconnectAttemptLimit is required for the preferred warm standby group and the fallbackWithinWSBGroup configuration must be disabled.
Summary
Application resilience is vital in the financial sector to maintain uninterrupted service, especially for real-time data delivery. The Real-time SDKs support various resilience features, including connection recovery, failover, warm standby, and the newly introduced Preferred Host. This feature, available from RTSDK C++/C Release 2.2.3.L1, allows consumer applications to specify a preferred host or standby group for seamless reconnection. It enhances reliability and supports mechanisms like failover, warm standby groups, and request routing, with configuration options available in both EMA and ETA Value Added.
Get In Touch
Related APIs
Related Articles
-
Introduction to the Real-Time SDK Request Routing Feature
-
Introduction to the Refinitiv Real-Time SDK Warm Standby Feature
-
How to Run Refinitiv Real-Time SDK C/C++ Warm Standby Examples
-
Introduction to Interactive Source Blending (ISB) feature in ADH 3.0 or above using EMA C++
-
Resiliency in real-time feed applications
-
Learn how to create auto-expiring records on Refinitiv Real-Time
-
Publish Custom Data via Refinitiv Real-Time Distribution System by EMA
Request Free Trial
Call your local sales team
Americas
All countries (toll free): +1 800 427 7570
Brazil: +55 11 47009629
Argentina: +54 11 53546700
Chile: +56 2 24838932
Mexico: +52 55 80005740
Colombia: +57 1 4419404
Europe, Middle East, Africa
Europe: +442045302020
Africa: +27 11 775 3188
Middle East & North Africa: 800035704182
Asia Pacific (Sub-Regional)
Australia & Pacific Islands: +612 8066 2494
China mainland: +86 10 6627 1095
Hong Kong & Macau: +852 3077 5499
India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Maldives & Sri Lanka:
+91 22 6180 7525
Indonesia: +622150960350
Japan: +813 6743 6515
Korea: +822 3478 4303
Malaysia & Brunei: +603 7 724 0502
New Zealand: +64 9913 6203
Philippines: 180 089 094 050 (Globe) or
180 014 410 639 (PLDT)
Singapore and all non-listed ASEAN Countries:
+65 6415 5484
Taiwan: +886 2 7734 4677
Thailand & Laos: +662 844 9576
