Python RDP Library Test Client
- Overview
- Setup
- Code Intro
- Request Data
- The Response
- Command Line Arguments
- Example Runtime Scenarios
Before we begin, if you are not familiar with the Refinitiv Data Platform Library - you can discover more by reading my earlier article (see Links Panel on the right).
The Performance
When I demonstrate or talk about our new Refinitiv Data Platform library to developers, I often get asked about its performance characteristics - particularly concerning to Realtime streaming data - 'how performant is it?','how many RICs can I consume at once?' and so on.
The simple answer to the above questions is 'it depends' - as there are too many factors at play to provide any meaningful answer. Things like your environment, your internet connection, your choice of instruments, their volatility, size of update messages e.t.c
The RDP Library is not meant for high-performance Realtime streaming implementations - ones requiring the lowest latency and/or highest throughput - for that you should be looking at our C++ and Java Refinitiv Real-Time SDKs
However, for less demanding scenarios, the RDP library offers a good balance of ease of use vs performance. I have done some basic testing on my laptop and was able to stream 3000 LSE RICs without any issues - having said that, I was merely dumping the payloads to a file and not doing any further processing. I was not trying to push or test any limits.
What I advise those developers who are curious, is to test the library for themselves using their mix of instruments, on their hardware and environment - which should provide a more meaningful picture.
To aid in this testing, I decided to share this relatively simple test tool (that I have been using myself), which I realised could also serve as an educational example - to illustrate various bits of the RDP Library's Realtime streaming data functions such as:
- RDP(Cloud), ADS(Deployed) or Eikon/Workspace(Desktop) connectivity
- Batch / View Request
- Streaming / Snapshot
- Reuters Domain Models
The example also provides:
- Basic stats
- Output to a log file
- Low-level Debugging
For full disclosure - the code is derived from an earlier Websocket API example I created with similar functionality.
The Setup & Requirements
Windows/Linux/macOS
- Install Python
- Go to: https://www.python.org/downloads/
- Select the Download tile for the Python 3 version
- Run the downloaded python-<version> file and follow installation instructions
- Install libraries
- This example has been revised to use the latest (at the time of writing) alpha version 1.0.0.a5 of the Python library.
- Run the following to install the 'refinitiv.dataplatform' library: pip install refinitiv-dataplatform=1.0.0a5
- See the source code for the other Python libraries you may need to install
- Credentials/Prerequisites - As a Refinitiv Customer, you should have access to at least one of the following:
- A desktop installation of Eikon or Refinitiv Workspace
- Details of an ADS Server
- the hostname/IP + port number of the ADS
- DACS username
- A Refinitiv Data Platform account
- RDP MachineID - found in your 'Welcome to Refinitiv - Your New Account' email
- RDP Password - set using the link in the above email
The AppKey
As well as one of the above, you will also need an AppKey - which can be generated either within Eikon or from our API Playground.
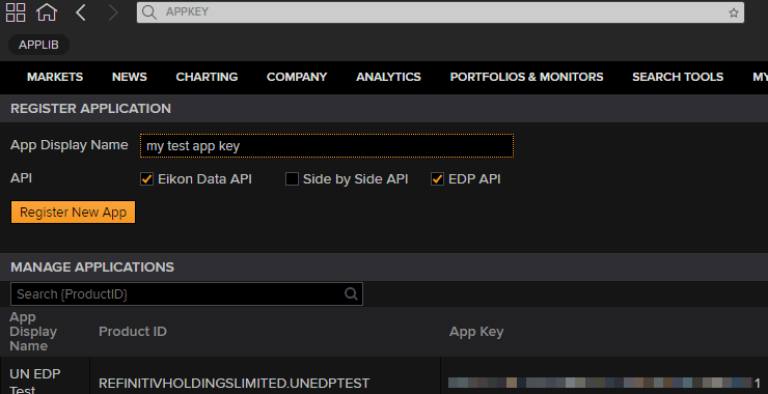
Within Eikon you can access the AppKey generator by searching for - you guessed it - 'APPKEY':
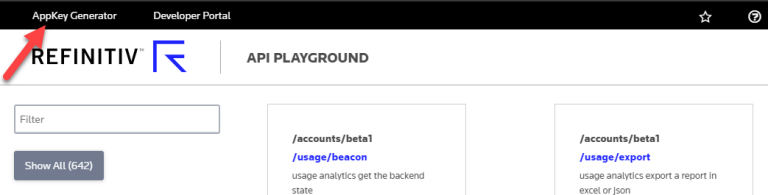
On the API Playground, you can access the generator by clicking the link in the top right corner:
Regardless of which of the above generators you use, ensure you tick the EDP API checkbox before clicking the Register New App button.
The Code
Now that I have the prerequisites out of the way, let me dive into the code...
Much of the code is standard Python code related to command line parameters etc and fairly self-explanatory - so I am going to focus mostly on the RDP Library specific snippets of code here.
Once the command line has been parsed and the parameters have been validated, the first thing we need to do is create our Session - i.e. connect to whichever data source we have chosen to use - Desktop, Cloud or Deployed.
Depending on the choice of session, I need to call one of the following:
# Connect to Eikon/Workspace
my_session = rdp.DesktopSession(
appkey,
on_state=lambda session, state, message: print("Desktop session state: ", state, message),
on_event=lambda session, event, message: print("Desktop session event: ", event, message)))
# Connect to an ADS
my_session = rdp.PlatformSession(
app_key=appkey, grant=None,
deployed_platform_host=host,
deployed_platform_username=user,
on_state=lambda session, state, message: print("Desktop session state: ", state, message),
on_event=lambda session, event, message: print("Desktop session event: ", event, message)))
# Connect to the Refinitiv Data Platform (Cloud)
my_session = rdp.PlatformSession(
appkey, rdp.GrantPassword(
username=user,
password=password),
on_state=lambda session, state, message: print("Desktop session state: ", state, message),
on_event=lambda session, event, message: print("Desktop session event: ", event, message))
NOTE: the on_state and on_event lambda functions are optional - but I like the additional feedback they provide on the state of the session and any session related events - e.g. successful connection and login:
Platform session event: EventCode.StreamConnected WebSocket for streaming session 1 was opened to server: wss://amer-1.pricing.streaming.edp.thomsonreuters.com:443/WebSocket
Platform session event: EventCode.StreamConnected Login accepted by host ads-premium-az1-green-14-main-prd.use1-az1.
In addition to the above state and event messages, you can optionally enable low-level logging for the session.
my_session.set_log_level(logging.DEBUG)
I normally only activate the debug logging when I am trying to diagnose a particular issue - otherwise, your console output can be flooded.
So, now that I have my session, I need to go ahead and establish the session:
my_session.open()
Single or Multiple Sessions?
One thing I should point out is that with the above usage, I obtained my session first and then opened it. This can be useful if you want to create multiple sessions within your application e.g. to consume data from both RDP and your ADS. You might want to do this if you need to combine data from Refinitiv with some data published internally within your organisation.
If you are just using a single session (and not interested in the state and event messages), you could use the simpler alternatives which obtain and open the session in a single call:
rdp.open_desktop_session(appkey)
#OR
rdp.open_platform_session(
appkey,
rdp.GrantPassword( username = user, password = password)
)
#OR
rdp.open_platform_session(
appkey,
deployed_platform_host = host,
deployed_platform_username = user
)
As this is meant to be a test tool, I want to capture the state and event messages - hence why I am not using the simpler alternatives.
Request my data
Once my session is open, I can go ahead and request my market data.
The code for making the request and processing the responses is in the market_data.py file, so before I proceed I need to pass across the request attributes specified on the command e.g. Service name to request the data from, list of RICs, domain model, snapshot mode etc.
NOTE: for RDP and Eikon/Workspace connections you do not need to specify a Service name - as they both have a default one configured. For ADS connections, check with your internal Market Data team if they have a default Websocket Service configured - if not ask them to provide you with the correct Service name.
Also, if a subset of fields (a View) was specified I need to pass that too. A View request is useful if you don't really need all the fields available for an instrument - e.g. if you only want the basic pricing field such ask Bid, Ask, Trade Price etc.
# Set request attributes
market_data.set_request_attr(opts.service, simple_rics, opts.domain, opts.snapshot, ext_rics)
# Set Field list if specified
if opts.view_names is not None:
view_list = opts.view_names.split(',')
market_data.set_view_list(view_list)
# Call my Request data method
market_data.request_data(my_session)
# Where request_data looks like:
def request_data(req_session):
global start_time
start_time = time.time()
""" Send items request """
if domain_ric_list:
send_multi_domain_data_request(req_session)
else:
send_single_domain_data_request(req_session, domain_model, simple_ric_list)
First I initialise my start_time so I can generate some basic stats later. Next, I check to see if the user has specified a multi-domain list of RICs via the -ef parameter - in which case I will request each RICs by its specified domain. If, however, the user has only specified a single domain on the command line, I can just request all the RICs using the single domain.
NOTE: Just in case you are not familiar with Domains:
- The default domain in MarketPrice i.e. Quote and Trade price data.
- We also support other domains such as MarketByPrice, MarketByOrder - for full depth order books
- As well as other domains such as NewsTextAnalytics - which includes Machine Readable News and Analytics
The above are some of the Domains that are supported by Refinitiv Realtime data.
I will skip the code for send_multi_domain_data_request - it is standard Python code which repeatedly invokes my send_single_domain_data_request method for each Domain specified in the multi-domain RIC file:
def send_single_domain_data_request(req_session, req_domain, ric_list):
global request_cnt
""" Create and send Market Data request for a single Domain type"""
# increment the data items requested count
request_cnt += len(ric_list)
for ric in ric_list:
stream = rdp.OMMItemStream(session=req_session,
domain=req_domain,
name=ric,
fields=view_list,
service=service_name,
on_refresh=lambda s, msg: process_message(msg),
on_update=lambda s, msg: process_message(msg),
on_status=lambda s, msg: on_status(s, msg))
# Streaming or snapshot?
stream.open(with_updates=not snapshot);
First, I set my request counter for later stats generation & the Auto Exit (-e parameter) implementation.
After which I iterate through my list of RICs and request each one individually - by specifying:
- Service Name
- RIC code for the instrument
- any Fields specified for a View request
- the data Domain
- and event handlers for the RefreshMsg, UpdateMsg and StatusMsg types
I then set the with_updates parameter to true if the user has not specified snapshot mode - before calling open(), which submits the request to the server. With snapshot mode, the server will send the initial Image RefreshMsg - after which it will close the stream - so no further updates will be received.
Batch Requests
You may be wondering why I can't make a Batch request for multiple RICS in a single call - well, you can but only for the default MarketPrice domain - and my test tool needs to support the other domains.
Therefore, If you are dealing solely with MarketPrice domain requests, you could use the StreamingPrices object to make a Batch Request with something like the following:
streaming_prices = rdp.StreamingPrices(
universe = ric_list,
fields = view_list,
on_refresh = lambda streaming_price, instrument_name, fields :
process_message(streaming_price, instrument_name, fields),
on_update = lambda streaming_price, instrument_name, fields :
process_message(streaming_price, instrument_name, fields),
on_status = lambda streaming_price, instrument_name, status :
process_message(streaming_price, instrument_name, status),
on_complete = lambda streaming_price :
display_complete_snapshot(streaming_price)
)
Note that with a Batch Request, a separate event stream is established by the server for each valid instrument - and so the responses will arrive individually from the server - not as a Batch. This makes sense since each instrument can and will update independently of others.
The Response
For each RIC I request I expect to get at least one response message:
- For a valid RIC which I am permissioned for, I can expect to receive an initial RefreshMsg - which contains all the fields that are supported for that RIC (or a subset if I specified a View)
- For an invalid RIC / one which I am not permissioned for - a StatusMsg with details of why the server cannot service that request
Assuming I received a RefreshMsg, I can expect to receive further UpdateMsgs for that instrument - as and when there is any market activity for that instrument. I may also receive subsequent StatusMsg - for example, if an instrument goes Stale as some later point in time.
So, let's take a look at the code for process_message:
def process_message(message_json):
message_type = message_json['Type']
message_domain = "MarketPrice" # Default - as we dont get Domain in MarketPrice message
if 'Domain' in message_json:
message_domain = message_json['Domain']
# Process different Message Types
if message_type == "Refresh":
if not (('Complete' in message_json) and # Default value for Complete is True
(not message_json['Complete'])): # Only count Refresh If 'Complete' not present or True
image_cnt += 1 # Only for Data related Refresh i.e. not Login
elif message_type == "Update":
update_cnt += 1
elif message_type == 'Error': # Oh Dear - server did not like our Request
print("ERR: ")
print(json.dumps(message_json, sort_keys=True, indent=2, separators=(',', ':')))
cleanup()
# Cleanup and exit - if auto_exit and we have received response to all requests
if auto_exit and (request_cnt == image_cnt + closed_cnt):
cleanup()
- Extract the Message Type - e.g. Refresh, Update, Error
- Extract Domain if present - otherwise default to MarketPrice
- Update the relevant counter
- If Auto Exit was specified & we have received responses for all our requests then initiate shutdown
Note here that I am comparing the request count with image count + closed count - in case some of my RICs were rejected by the server. In which case I get a StatusMsg response - and for which I defined a separate handler function:
def on_status(item, status_msg):
global status_cnt, closed_cnt
status_cnt += 1
# Was the item request rejected by server & stream Closed?
if item.state == rdp.StreamState.Closed:
closed_cnt += 1
if auto_exit and (request_cnt == image_cnt + closed_cnt):
cleanup()
Once again I initiate a shutdown if Auto Exit was specified and we have received responses for all our requests.
If AutoExit was not specified, the application will continue to run indefinitely or until it reaches any -et exit time parameter value specified.
During the runtime, the application will generate basic stats every few seconds (default value of 5 - override with the -st parameter).
For example:
Stats; Refresh: 2641 Updates: 264 Status: 3000 Elapsed Time: 652.50secs
Stats; Refresh: 2641 Updates: 286 Status: 3000 Elapsed Time: 662.50secs
Stats; Refresh: 2641 Updates: 314 Status: 3000 Elapsed Time: 682.56secs
Stats; Refresh: 2641 Updates: 336 Status: 3000 Elapsed Time: 692.57secs
FYI: The above stats were for 3000 instruments (of which 2641 were valid/permissioned) requested from my laptop, over my home internet connection - from the Refinitiv Data Platform.
Closing Summary
I hope you find this example and the code walk-through useful for basic testing and as a simple guide to consuming Realtime data using the RDP library.
Just to recap, I described how the example allows you to
- connect to Refinitiv Real-Time, Eikon/Workspace or Refinitiv Data Platform
- consume individual items specified on the command line OR
- a list of RICs for a single domain OR
- a mixture of RICs for multiple domains
- optionally specify a subset of fields - i.e. View
- obtain some rough idea of the RDP library's performance in your environment
At present, whilst you can use the example to request NewsTextAnalytics domain for Machine Readable news etc, it does not collate + decode the responses into the final usable payload.
Additional Resources
You will find links to the Source code, Library and Related Articles in the Links Panel
Please find below a list of the various parameters and a few example usage scenarios:
Command-line arguments:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| -h, --help | Show this help message and exit |
| -S SERVICE | Service name to request from (default: ELEKTRON_DD) |
| -H HOST | ADS server hostname:port (default: None) |
| -ap APPKEY | AppKey / ClientID (default: None) |
| -u USER | MachinedID/username for RDP/ADS (default: None) |
| -pw PASSWORD | RDP user password (default: None) |
| -items ITEMLIST | Comma-separated list of RICs (default: None) |
| -fields VIEW_NAMES | Comma-separated list of Field Names for View (default:None) |
| -md DOMAIN | Domain Model (default: None - however, server defaults to MarketPrice) Accepts numeric or name e.g. 6 or MarketPrice, 7 or MarketByOrder, 8 or MarketByPrice |
| -f RIC_FILE | Simple file of RICs - one per line (default: None) |
| -ef EXT_RICFILE | Name of file containing multi-domain RICs - e.g. MarketByPrice|VOD.L (default: None) |
| -t | Snapshot request (default: False) |
| -X | Output Received Data to console (default: False) |
| -l LOG_FILENAME | Redirect console to filename (default: None) |
| -e | Auto Exit after all items retrieved (default: False) |
| -et EXIT_TIME_MINS | Exit after time in minutes (0=indefinite) (default: 0) |
| -st STATS_TIME_SECS | Show Statistics interval in seconds (default: 5) |
| -sos | Output received Status messages (default: False) |
| -dbg | Output low level debug trace (default: False) |
Example runtime scenarios
Below are a few example scenarios with sample arguments
Connect to Refinitiv Data Platform, request MarketPrice items from default service and display summary stats
-items VOD.L,BT.L -u <RDP Username> -pw <RDP Password> -ap <AppKey>
Connect to ADS, request MarketPrice items from ELEKTRON_DD service and display summary stats
-S ELEKTRON_DD -H ads1:15000 -items VOD.L,MSFT.O,TRI.N -u umer.nalla -ap <AppKey>
Connect to Eikon/Workspace, request MarketPrice items from default service and display summary stats
-ap <AppKey> -items VOD.L,MSFT.O,TRI.N
Request MarketPrice items from default service on ADS (if one has been configured) and display summary stats
-H ads1:15000 -items VOD.L,MSFT.O,TRI.N -u umer.nalla -ap <AppKey>
As above and display received data
-H ads1:15000 -items VOD.L,MSFT.O,TRI.N -u umer.nalla -X -ap <AppKey>
As above with output redirected to file log.out
-H ads1:15000 -items VOD.L,MSFT.O,TRI.N -u umer.nalla -X -l log.out -ap <AppKey>
As above except request MarketByPrice data
-H ads1:15000 -md MarketByPrice -items VOD.L,BT.L,BP.L -u umer.nalla -X -l log.out -ap <AppKey>
As above except using numeric Domain value
-H ads1:15000 -md 8 -items VOD.L,BT.L,BP.L -u umer.nalla -X -l log.out -ap <AppKey>
MarketPrice request for RICs read from file srics.txt (one RIC per line)
-H ads1:15000 -f srics.txt -u umer.nalla -X -l log.out
MarketByOrder request for RICs read from file srics.txt (one RIC per line)
-H ads1:15000 -f srics.txt -md MarketByOrder -u umer.nalla -X -l log.out
As above except mixed Domain RICs read from file extrics.txt (numeric domain|RIC per line)
-H ads1:15000 -ef extrics.txt -u umer.nalla -X -l log.out
I have provided the example srics.txt and extrics.txt files for your reference
Disclaimer
The source code presented in this project has been written by Refinitiv solely to illustrate the use of the RDP Library interface. None of the code has been tested for usage in production environments.