

Introduction
Have you wondered how much usage you have left until it's exceed the limit? To prevent the user from experiencing issues due to abnormal or excessive usage, the LSEG Data Library applies usage limits. You can find the official guidelines in Documentation | Devportal
Currently, you can check your Data Library usage by enabling debug logging in the Workspace Application and inspecting the HTTP response headers. This article walks you through the process, including how to use monkey-patching to print out response headers directly from your Python code.
Note: I'm using LSEG Data Library for Python version 2.1.1 here
Step 1: Enable Debug Logging in LSEG Workspace
1. Open the Configuration Manager in your LSEG Workspace Application.
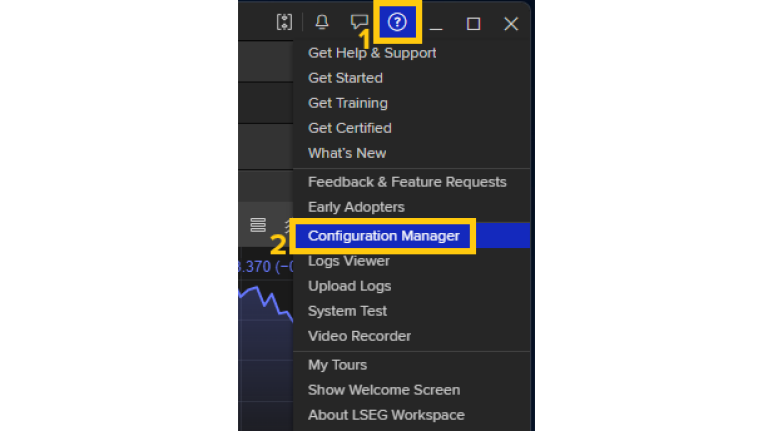
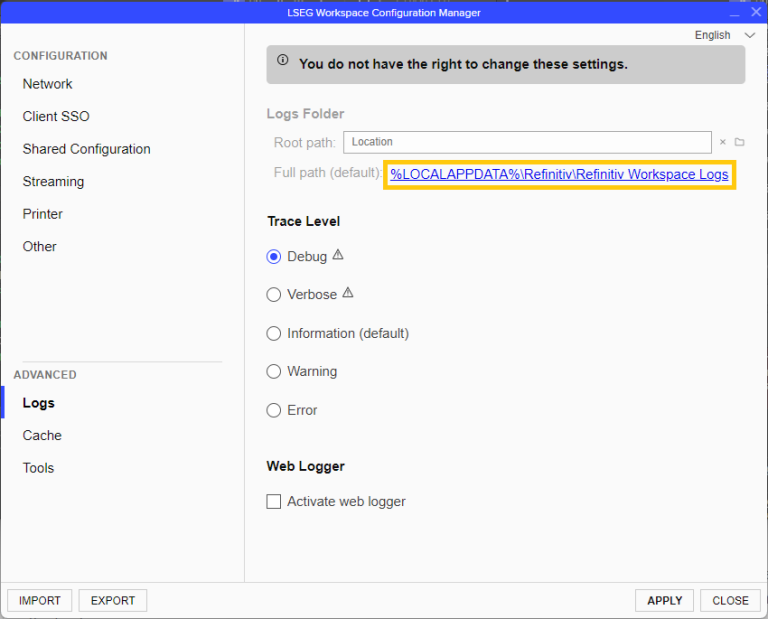
2. Navigate to the Logs page under the Advanced section.
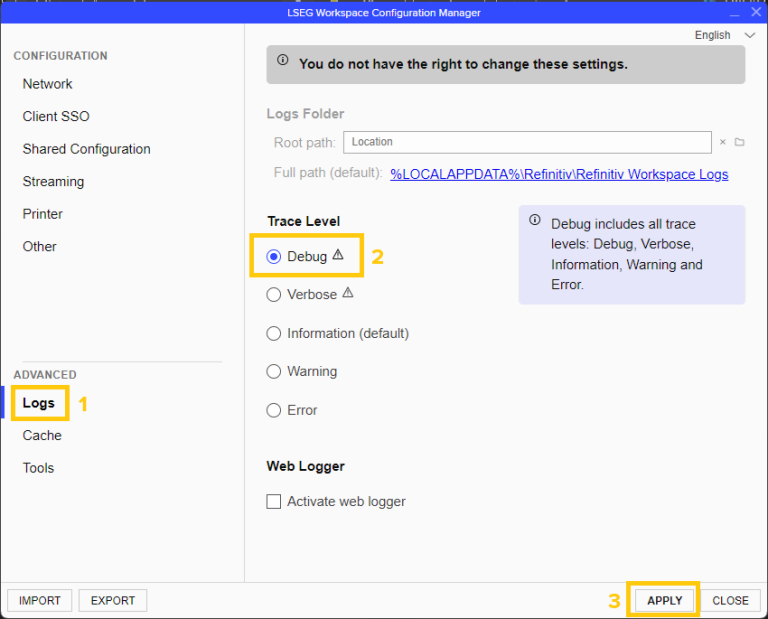
3. Set the Trace Level to Debug, then click Apply (see screenshot below)
Note: Setting the trace level to Debug may impact system performance. Use this level only when troubleshooting or monitoring usage.
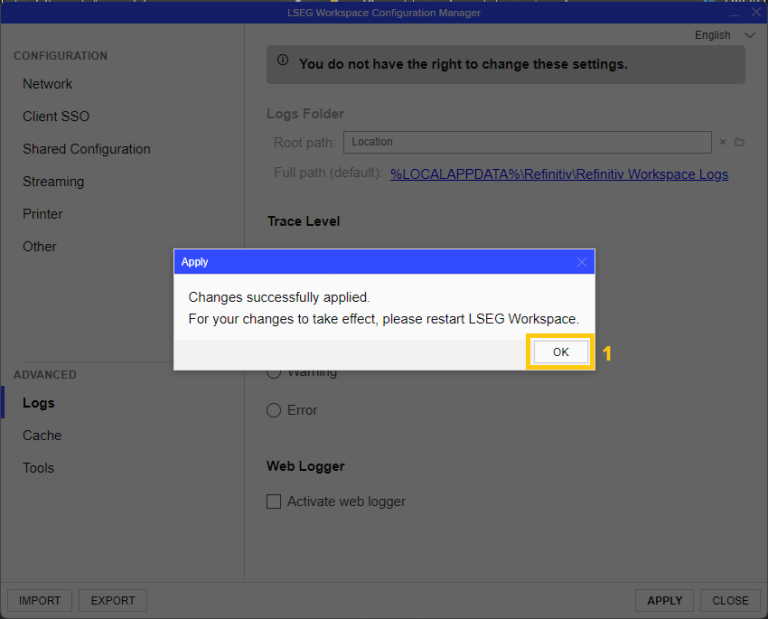
4. Click OK to apply the configuration and Restart LSEG Workspace to activate the changes.
Step 2: Configure Logging in Your Python Script
You can set the log level to debug either in your configuration file or directly in your code. Here’s the example configuration file: (see more detail and example of configuration file here)
{
"logs": {
"level": "debug",
"transports": {
"console": {
"enabled": true
},
"file": {
"enabled": true,
"name": "lseg-data-lib.log"
}
}
},
"sessions": {
"default": "desktop.workspace",
"desktop": {
"workspace": {
"app-key": "<YOUR APP KEY>"
}
}
}
}
And here's how to do it in-line:
import lseg.data as ld
config = ld.get_config()
config.set_param("logs.transports.console.enabled", True)
# config.set_param("logs.transports.file.enabled", True) # Uncomment to log to file
config.set_param("logs.level", "debug")
ld.open_session()
Step 3: Monkey-Patch the Data Library to Log HTTP Response Headers
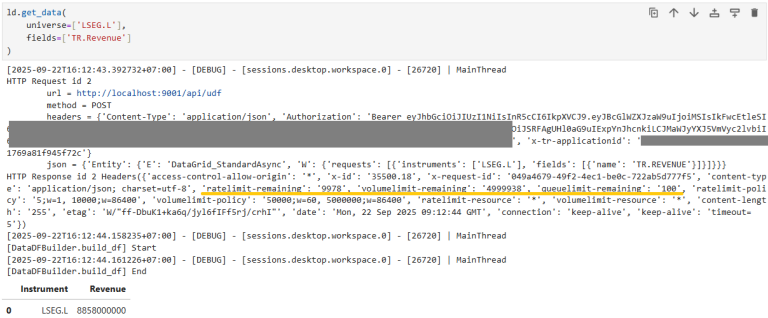
To print out the HTTP response headers (which often include usage and limit information), you can monkey-patch the request method in the HTTPService class:
import lseg.data._core.session.http_service as http_service
from httpx import Response
# Save original method if needed
original_request = http_service.HTTPService.request
# Define your custom version
def custom_request(self, request):
response: Response = self._client.send(request)
print(f"HTTP Response id {request.id} {response.headers}")
return response
# Monkey-patch the method
http_service.HTTPService.request = custom_request
Step 4: Run Your Data Retrieval Code
Now, when you run your Data Library functions to retrieve data, the HTTP response headers—including any limit or usage information—will be printed in your console log (or log file, depending on your configuration).
Step 5: Check Detailed Logs in Workspace
For more detailed information about your API usage and limits:
- Go to the Workspace Logs folder. The Full Path to it can be found in Logs section of Configuration Manager
- Open the most recently created sub-folder named like Desktop.<date>.<time>.p<process-ID>.
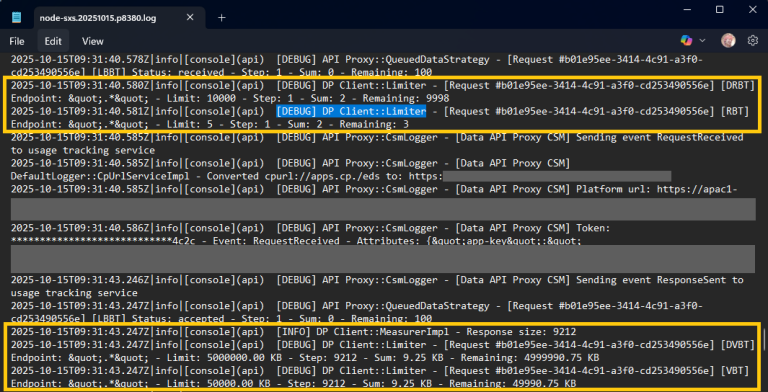
- Look for the file named node-sxs.<date>.p<process-ID>.log.
- Search for the lines that contains [DEBUG] DP Client::Limiter
Here, you can find additional details about your requests and any limit-related messages.
Conclusion
By enabling debug logging and monkey-patching the LSEG Data Library, you can easily monitor your API usage and remaining limits in real time. This approach helps you stay within your quotas and troubleshoot issues more effectively.
The sample Jupyter Notebook file for this article can be found in the top right section of this article.
Get In Touch
Related APIs
Related Articles
Source Code
Request Free Trial
Call your local sales team
Americas
All countries (toll free): +1 800 427 7570
Brazil: +55 11 47009629
Argentina: +54 11 53546700
Chile: +56 2 24838932
Mexico: +52 55 80005740
Colombia: +57 1 4419404
Europe, Middle East, Africa
Europe: +442045302020
Africa: +27 11 775 3188
Middle East & North Africa: 800035704182
Asia Pacific (Sub-Regional)
Australia & Pacific Islands: +612 8066 2494
China mainland: +86 10 6627 1095
Hong Kong & Macau: +852 3077 5499
India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Maldives & Sri Lanka:
+91 22 6180 7525
Indonesia: +622150960350
Japan: +813 6743 6515
Korea: +822 3478 4303
Malaysia & Brunei: +603 7 724 0502
New Zealand: +64 9913 6203
Philippines: 180 089 094 050 (Globe) or
180 014 410 639 (PLDT)
Singapore and all non-listed ASEAN Countries:
+65 6415 5484
Taiwan: +886 2 7734 4677
Thailand & Laos: +662 844 9576
