| Tutorial Source Code | Historical Pricing Workbook |
| Last Update | April 2025 |
| Language | VBA |
| Compiler | Microsoft Visual Basic Editor (VBE) |
| Pre-requisites | LSEG Workspace / Workspace for Excel installed Dll installation |
Overview
The following tutorial demonstrates API access to the Historical Pricing content using VBA within Microsoft Excel. The code segments will summarize the interfaces as demonstrated within the tutorial source available within the Excel Workbook.
The Historical pricing API is used to retrieve Intraday, Interday and events-based timeseries bars. Requests can be filtered by types, including start time, end time, and market session durations. Events-based requests can be filtered by types including trades, quotes or corrections.
Historical Pricing
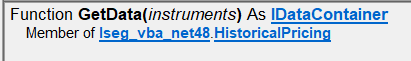
The HistoricalPricing interface replicates the Excel Addin RDP.HistoricalPricing() where the following is defined within the Object Browser:
With so many options and properties available when choosing to retrieve historical pricing data, HistoricalPricing supports a fluent interface using VBAs With...End With block providing simple access to pull down the desired bars.
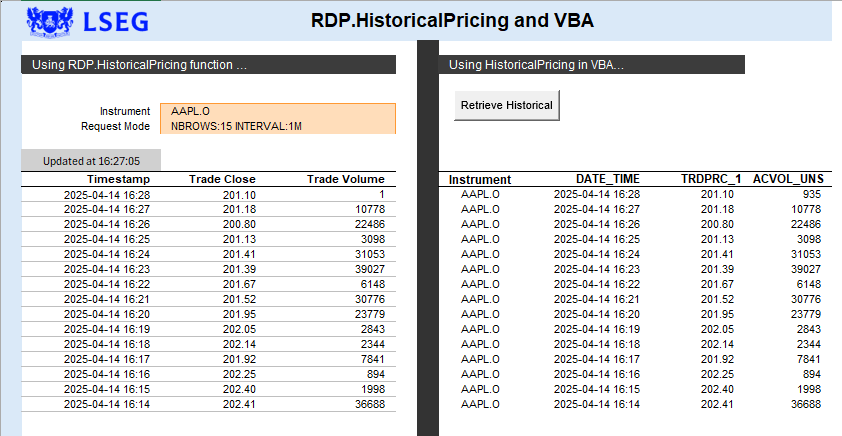
Let's consider the following example within the Historical Pricing Workbook:
' Utilize the cell-referencing mechansim to present data to the sheet
Sub HistoricalRequest_DefaultDisplay()
Dim history As New HistoricalPricing
Dim startCell As Range: Set startCell = [HistoryCellVBA]
On Error GoTo errHandler
' Clear the data region
[VBARegion].ClearContents
[VBARegion].ClearComments
With history
.fields Array("TRDPRC_1", "ACVOL_UNS")
.RequestMode [RequestMode]
.TimestampLabel TimestampEnum.TimestampEnum_endPeriod
.DisplayCell startCell
.GetData [RHistoryItem].Value
End With
Exit Sub
errHandler:
HandleError err, startCell
End Sub
The example worksheet provides a side-by-side comparison of using the Excel Add-in RDP.HistoricalPricing() and the code used within VBA using the HistoricalPricing interface. While their are many similarities between the two, the HistoricalPricing closely aligns with the HPA (Historical Pricing API) provided within the back-end but also includes some value added features similar to the RDP.HistoricalPricing(), such as the Request Mode options. In addition, the VBA code includes a cell-referencing feature, via the DisplayCell property allowing easy and simple display and testing of the capability. In many cases this can be ideal, especially if developers wish to quickly confirm the requested data. It can also be easily used as reference point to pull out content for worksheet calculations.
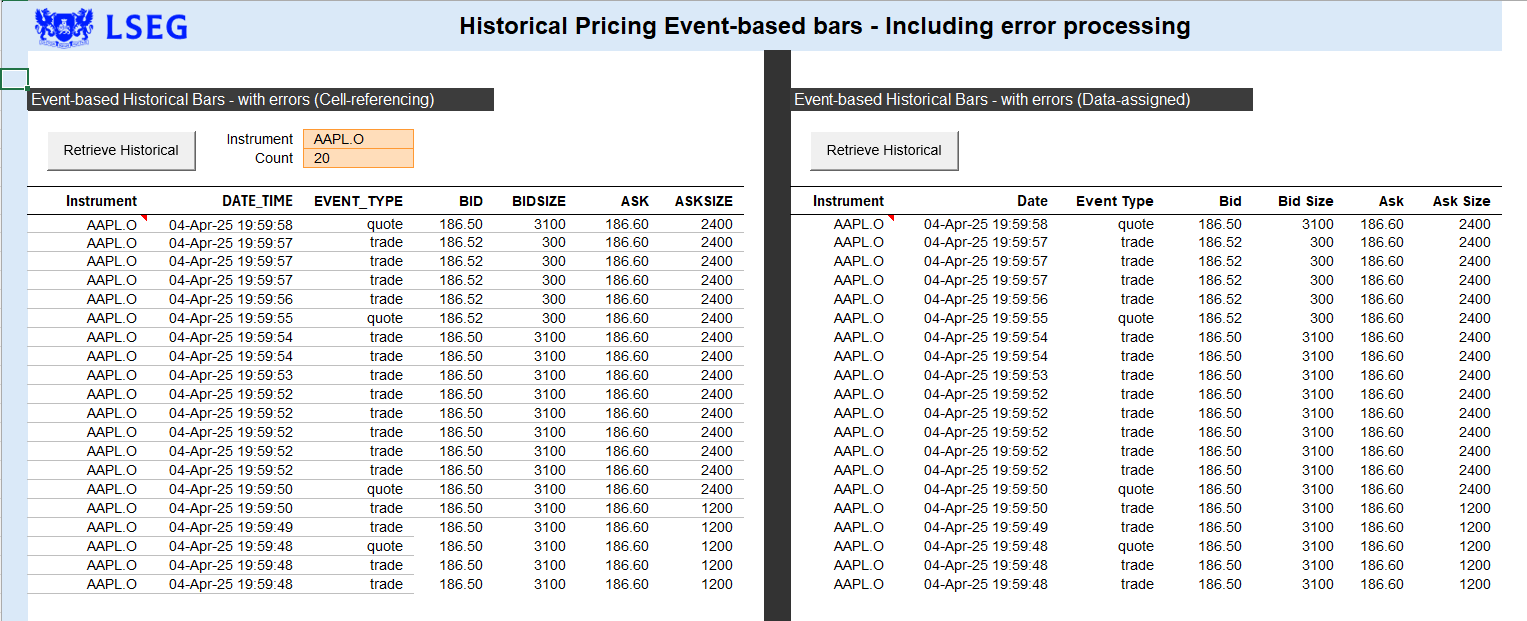
As you can see from the code snippet above, there is no requirement to retrieve and process the results, although this capability is present. For example, consider this example:
Sub HistoricalRequest_Error_MessageProcessing()
Dim history As New HistoricalPricing
Dim result As IDataContainer
Dim data, errors As Variant
Dim startCell As Range: Set startCell = [HistoryCell2]
Dim i As Integer, j As Integer
On Error GoTo errHandler
' Clear the data region
[ErrorDataRegion].ClearContents
[ErrorDataRegion].ClearComments
With history
.Interval IntervalEnum_EVENTS
.fields Array("EVENT_TYPE", "BID", "BIDSIZE", "ASK", "ASKSIZE")
.Count [ErrorCount].Value
Set result = .GetData([ErrorItem].Value)
End With
' Process the results - 2D-array
' Note: For this example, I'm not displaying the headers but relying on the spreadsheet header details.
data = result.data
For i = LBound(data, 1) + 1 To UBound(data, 1)
For j = LBound(data, 2) To UBound(data, 2)
If IsEmpty(data(i, j)) Then
startCell.Offset(i - 1, j).Value = CVErr(xlErrNA) ' Set to #N/A
Else
startCell.Offset(i - 1, j).Value = data(i, j)
End If
Next j
Next i
' Process the errors - 1D-array of IErrorCell
errors = result.errors
For i = LBound(errors) To UBound(errors)
Dim error As IErrorCell
Set error = errors(i)
If UBound(data) <= 0 Then
startCell.Offset(i, 0).Value = "Error"
End If
startCell.Offset(i, 0).AddComment (error.message)
Next i
Exit Sub
errHandler:
HandleError err, startCell
End Sub
The code segment above, which represents the example labeled as "Data-assigned", is more involved now that we're returning and processing a result. The IDataContainer defines 2 properties:
- data
The data property is a 2-D array of Variant values representing the header, rows and columns of data you see displayed. - errors
A 1-D array of IErrorCell objects.
An IErrorCell interface defines the following properties:
- row
Row containing error - column
Column containing error - item
Related instrument - message
Error message
With our resulting IDataContainer, we simply iterate through the data and errors section of the response to display values to the worksheet.
As you can see from the HistoricalPricing interface, there are a number of properties available for experimentation. The HistoricalPricing workbook provides additional examples and will continue to expand to demonstrate some of the different capabilities offered.